侯捷老师-C++课件_面向对象高级编程:链接
什么是深复制?什么是浅复制?(深拷贝与浅拷贝)
参考链接:深拷贝与浅拷贝
经典分类
模板(class template)
1 | template<typename T> |
内联函数(inline)
函数在类本体内定义则是内联函数,否则不是。所有函数都可以写成inline,但有些函数定义为inline,但是编译器没有能力将他做成inline。(函数过于复杂则不能)
访问级别
private层变量只能class本体成员函数访问。
构造函数
- 创建一个对象时候,一个函数会自动调用起来,这个函数就是构造函数。
- 构造函数没有返回值。
- 构造函数可以有默认值。
- 初始化参数:仅构造函数才享有。
构造函数有两个阶段:
- 初始化阶段。(这就是初始化参数的效果,如果不那样做,就等于放弃了初始化阶段,从而效率变差。)
- 赋值阶段。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22class complex
{
public:
complex (double r = 0, double i = 0) : re (r), im (i) { } //初始化参数
/*
相当于 complex (double r = 0, double i = 0) { re = r; im = i; }
*/
complex& operator += (const complex&);
double real () const { return re; }
double imag () const { return im; }
private:
double re, im;
friend complex& __doapl (complex*, const complex&);
};
{
complex c1(2, 1);
complex c2;
complex* p = new complex(4);
...
}
构造函数可以有很多个-overloading(重载)
1 | double real () const { return re; } |
1 | class complex |
构造函数放在private区
singleton:外部只有一个接口访问这个类,单例模式。
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
public:
static A& getInstance();
setup() { ... }
private:
A();
A(const A& rhs);
...
};
A& A::getInstance() {
static A a;
return a;
};调用时候,不能用传统方式A a(); 只能用A::getInstance().setup();
常量成员函数(const member functions)
函数分为内部改变数据的与内部不会改变数据的。不会改变数据的则最好使用const。
2
double imag() const { return im; }
函数该加const时候不加const的后果
这样调用是ok 的。1
2
3
4
5{
complex c1(2, 1);
cout << c1.real();
cout << c1.imag();
}
下面这种情况不加,当c1.real()执行时,real()函数后面没有加const,此时,c1.real()语句是const,不能更改,然后real()函数会发生更改,所以会导致编译器错误。1
2
3
4
5{
const complex c1(2, 1);
cout << c1.real();
cout << c1.imag();
}
参数传递:pass by value vs. pass by reference(to const)
值传递:整个包都会传递过去,效率较差。
尽量所有参数都传引用。
传递速度很快,且不能更改:则pass by reference to const。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15class complex
{
public:
complex (double r = 0, double i = 0) : re (r), im (i) { } //初始化参数
/*
相当于 complex (double r = 0, double i = 0) { re = r; im = i; }
*/
complex& operator += (const complex&);
double real () const { return re; }
double imag () const { return im; }
private:
double re, im;
friend complex& __doapl (complex*, const complex&);
};
返回值传递:return by value vs. return by reference(to const)
1 | ostream& operator << (ostream& os, const complex& x) { |
友元(friend)
友元函数是可以直接访问类的私有成员的非成员函数。 它是定义在类外的普通函数,它不属于任何类,但需要在类的定义中加以声明,声明时只需在友元的名称前加上关键字friend。
参考链接:友元
2
3
4
5
ths->re += r.re; //自由取得friend的private成员
ths->im += r.im;
return *ths;
}
相同class 的各个objects互为friends(友元)
1 | class complex { |
操作符重载-1, 成员函数,this
1 | inline complex& __doapl(complex* ths, const complex& r) { |
return by reference 语法分析
传递着无需知道接受者是以reference形式接收
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
ths->re += r.re;
ths->im += r.im;
return *ths;
}
inline complex& complex::operator += (const complex& r) {
return __doapl (this, r);
}
操作符重载-2,非成员函数(无this)






类里面带着指针

1
2string s3(s1); //拷贝构造
string s3 = s2; //拷贝赋值

1
2
3
4
5 String(const String& str); //拷贝构造
String& operator=(const String& str); //拷贝赋值
private:
...
char* m_data; //最好写成动态形式

1
delete[] m_data; //析构清理

会导致内存泄露,制造野指针,变成孤儿(浅拷贝)。

深拷贝

三步:1、先分配空间。2、重新创造自己。3、拷贝过来。
必须要进行检测自我赋值。如果相同时候结果会出错,将原地址也清空了。






stack自动释放,而heap必须手动释放。


静态,作用域结束之后仍然存在。

全局作用域。


new分为三个动作:1、分配内存。2、转型。3、构造函数。

delete两个动作:1、析构函数。2、delete.









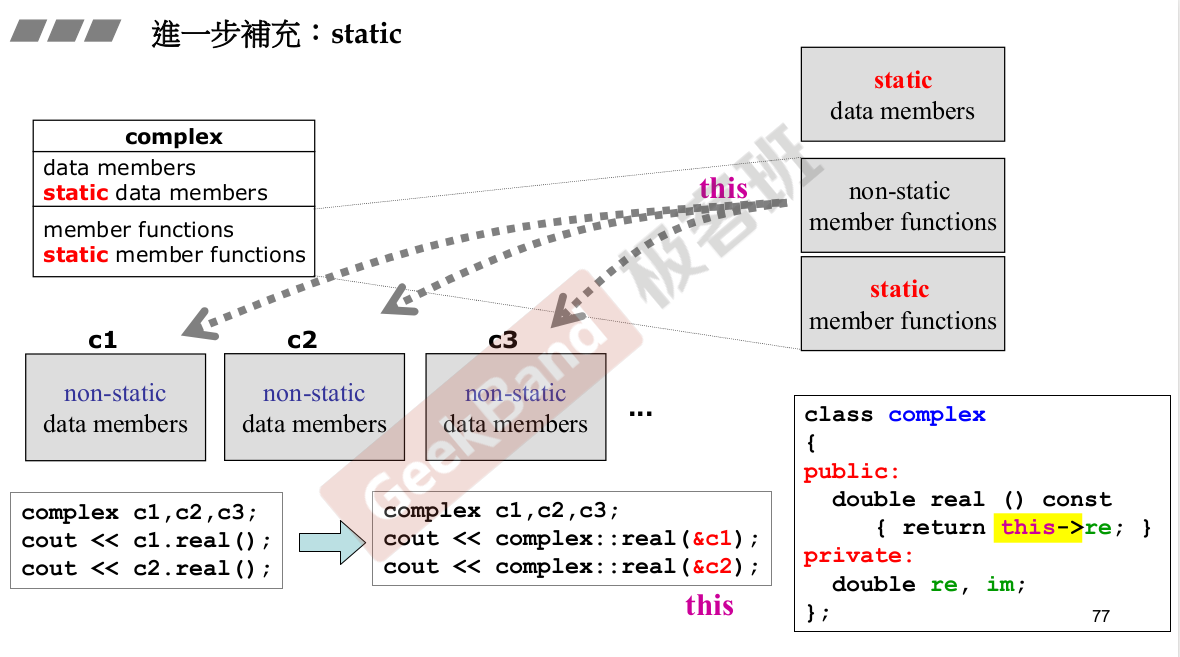
==>>后面是以c的调用。相同的函数传递的是不同的地址。成员函数有一个隐藏的this指针,可以在函数中去使用它,在参数列中不可以写。加上static后不属于某一个对象,只有一份。静态函数没有this指针,指针去存取静态数据,不能像一般成员函数那样存取一般数据成员。

静态数据一定要在类的外部设置初值(定义)。 静态函数只能处理静态数据。两种调用方式:类调用、对象调用。

这个才是更好的写法。有调用a 才会出现,使得资源不浪费。

生成的class只想产生一个对象。这里的A只有一份,设置静态函数使得与外界联系的唯一接口。这里如果没有创建a,则会浪费资源。
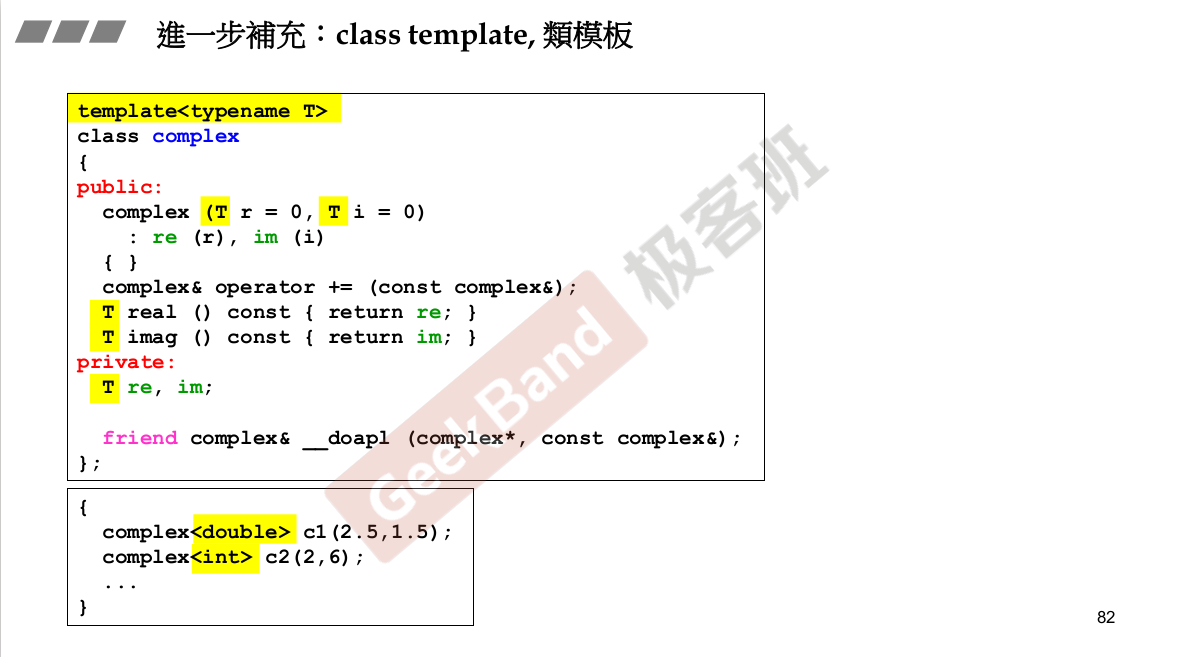
模板写法。T 只是一个符号而已。
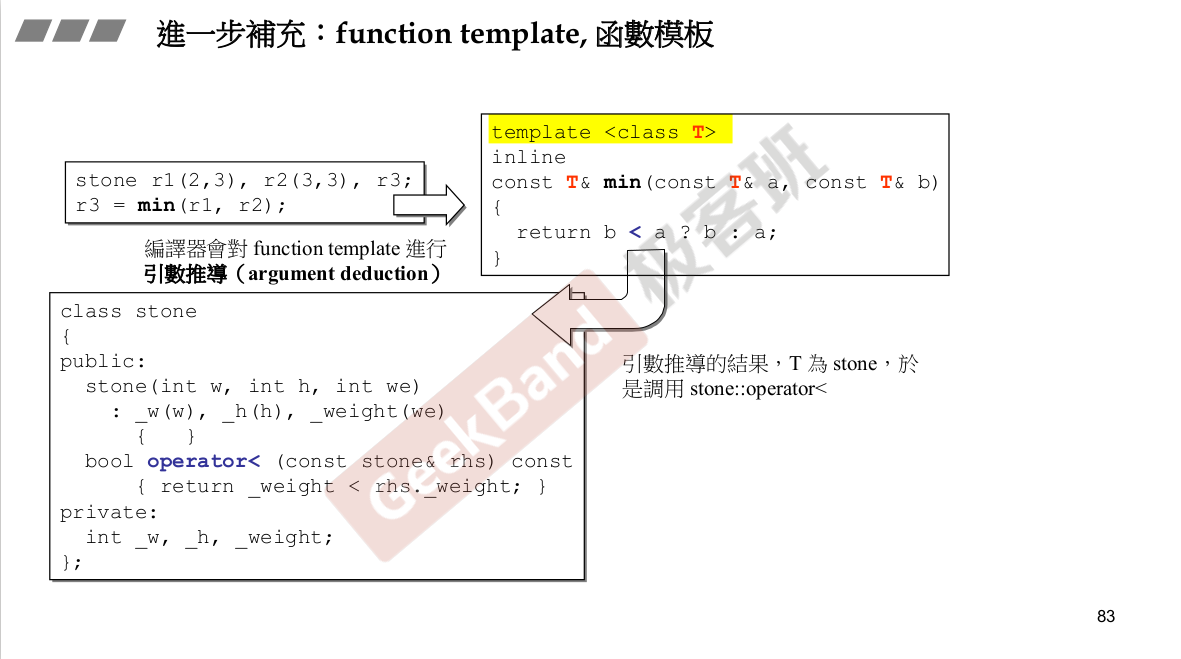
编译器会对函数模板进行参数推到。<操作符重载。
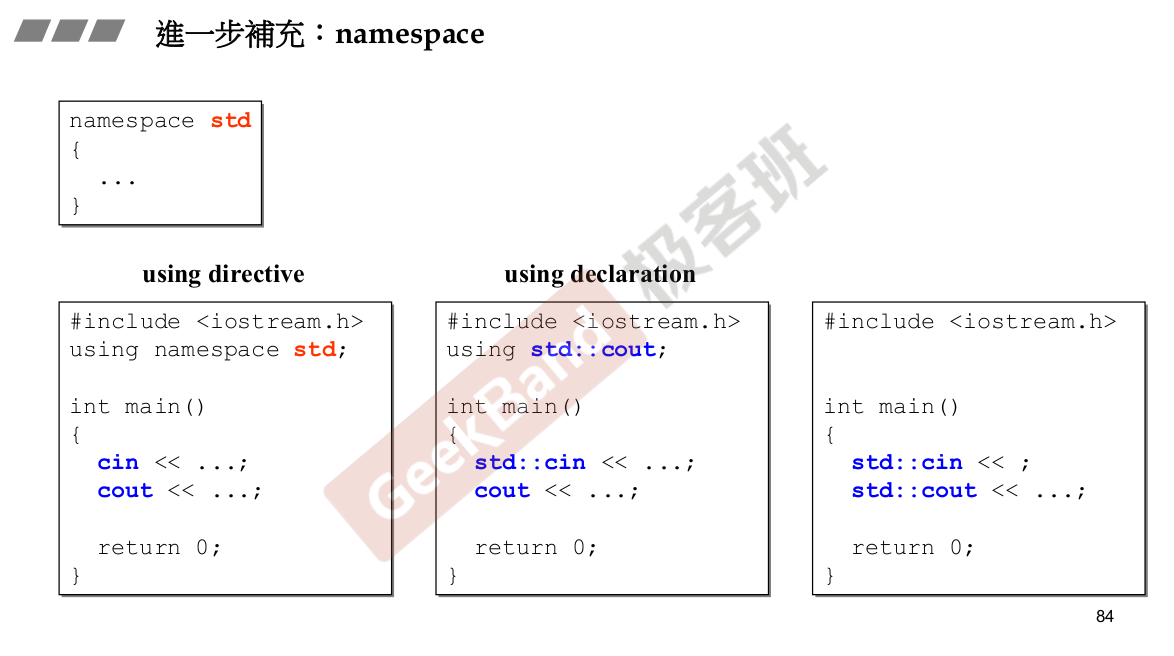
所有东西被包装一个namespace里面,防止自己写的与其他人写的重名。也可以不一下全部打开,一条一条的打开。




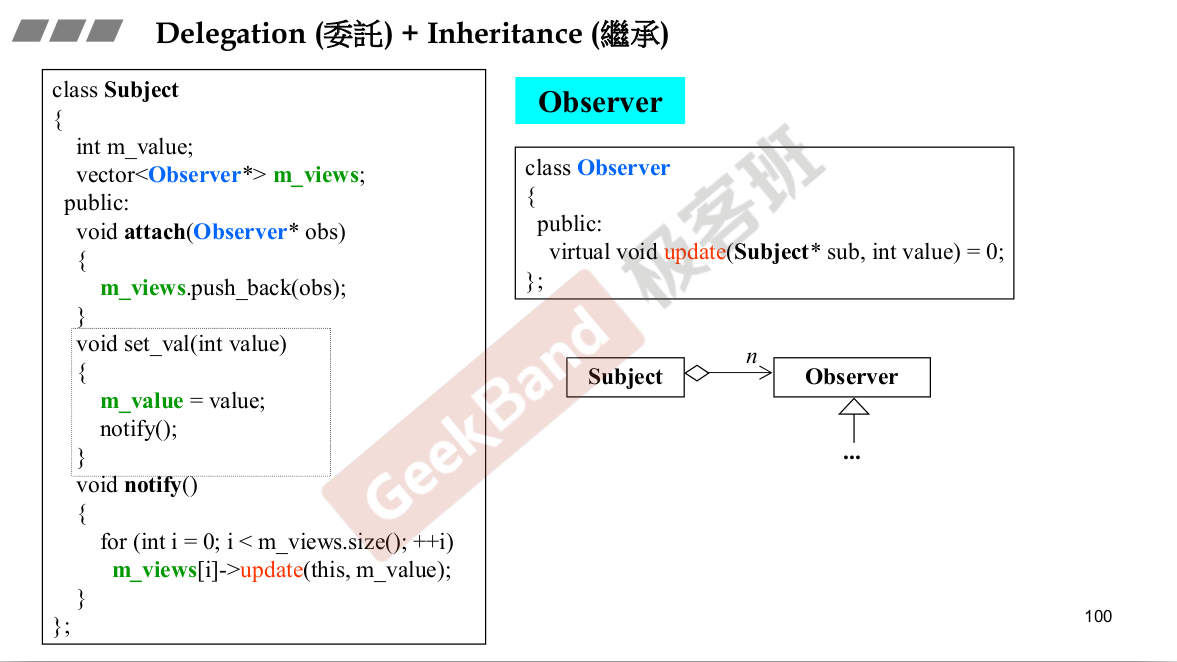
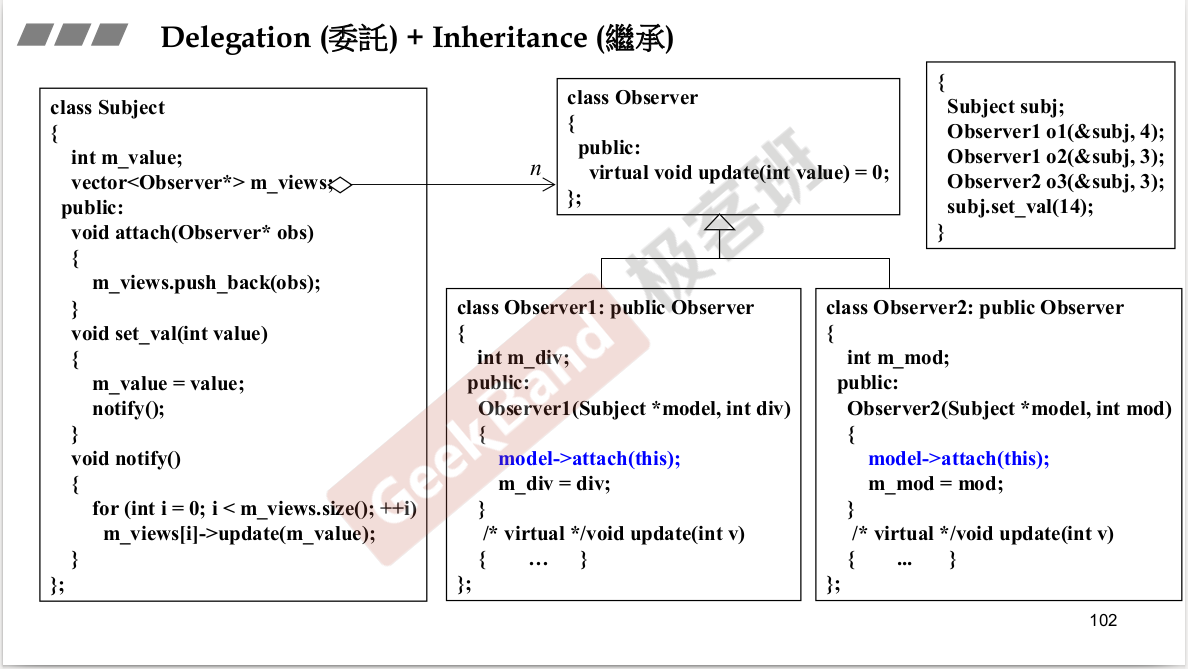
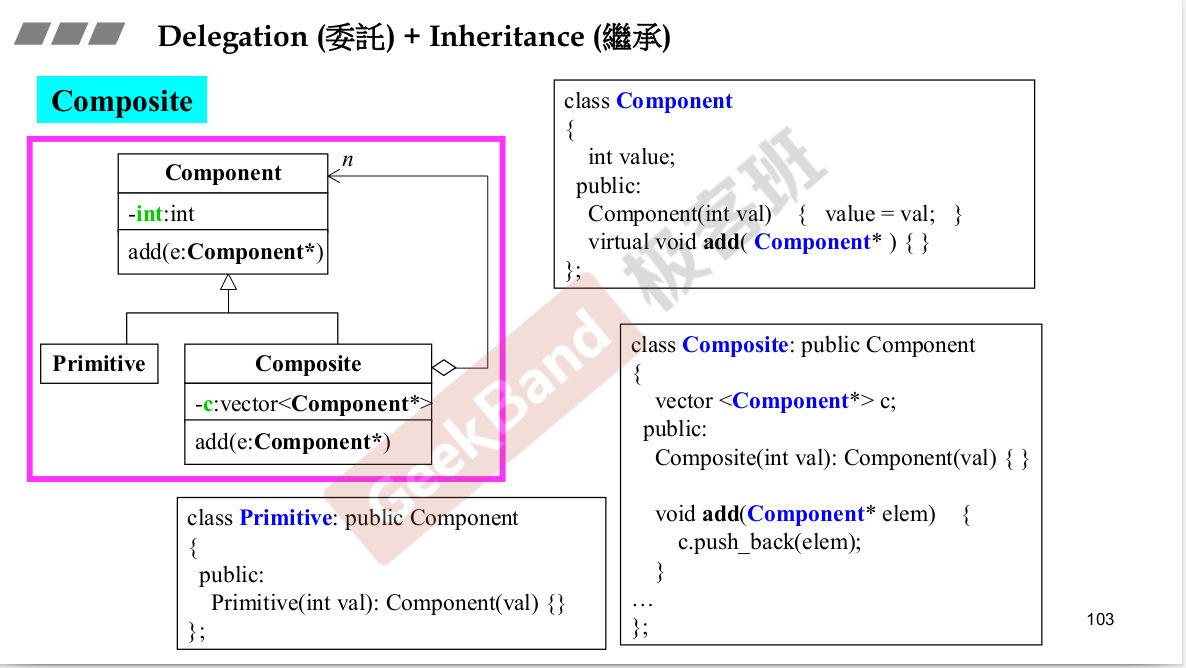
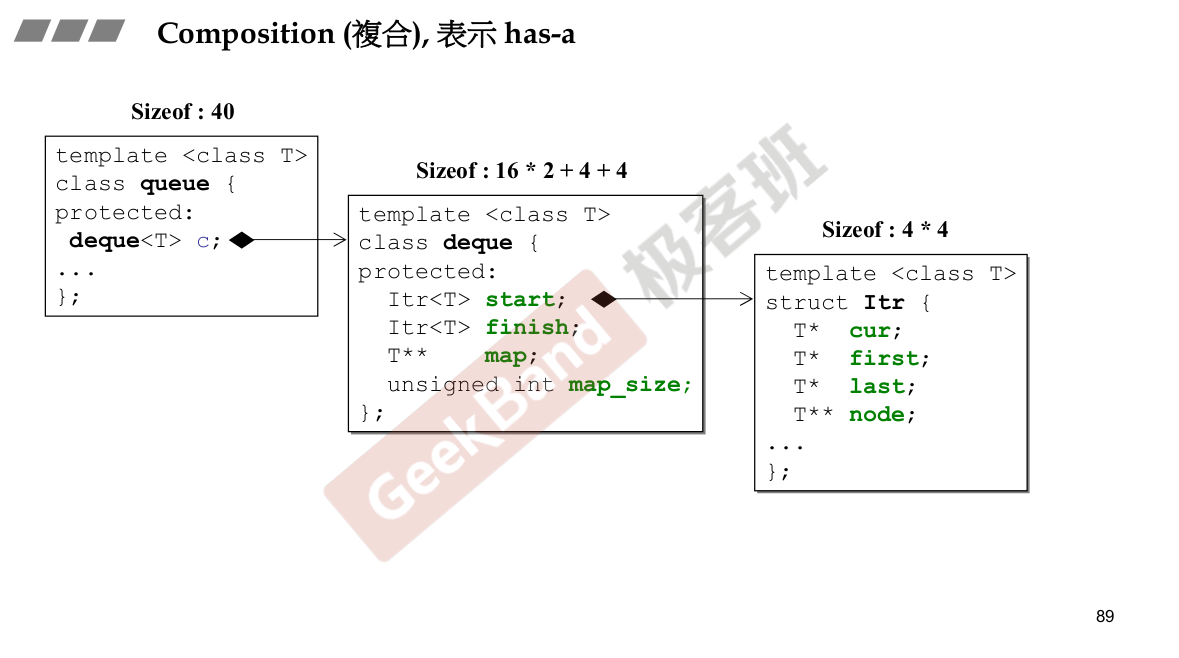
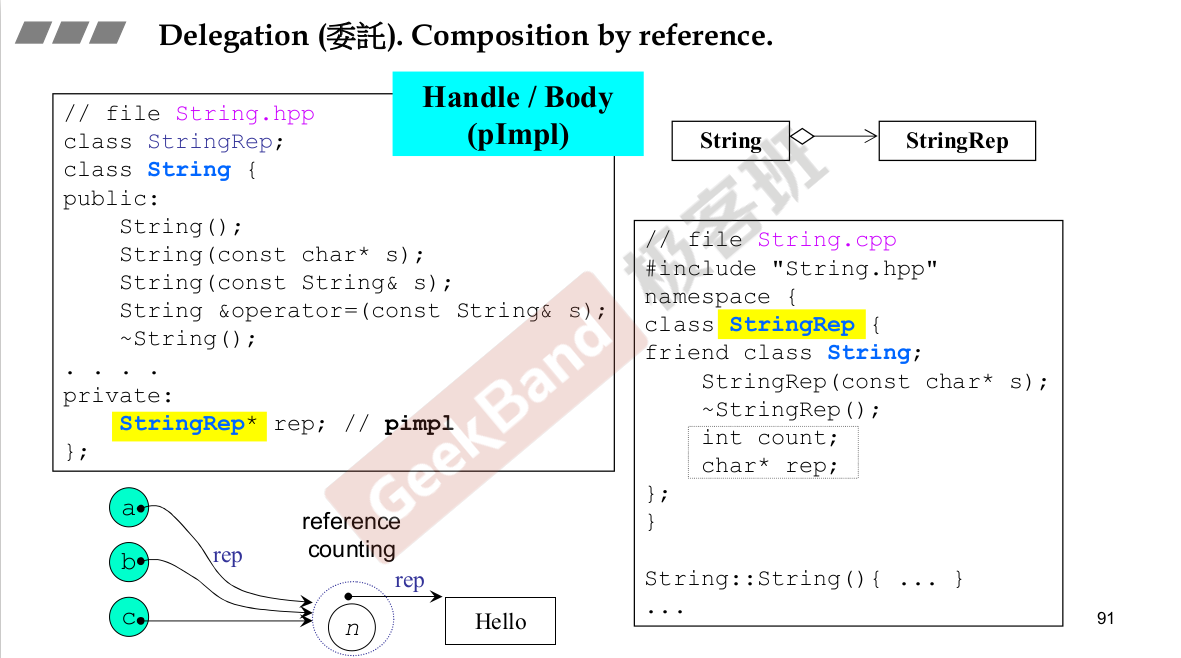
里面有另外一个东西。queue里面有一个deque。A has a B,A的功能让B去完成。
Adapter设计模式。queue是一个Adapter.
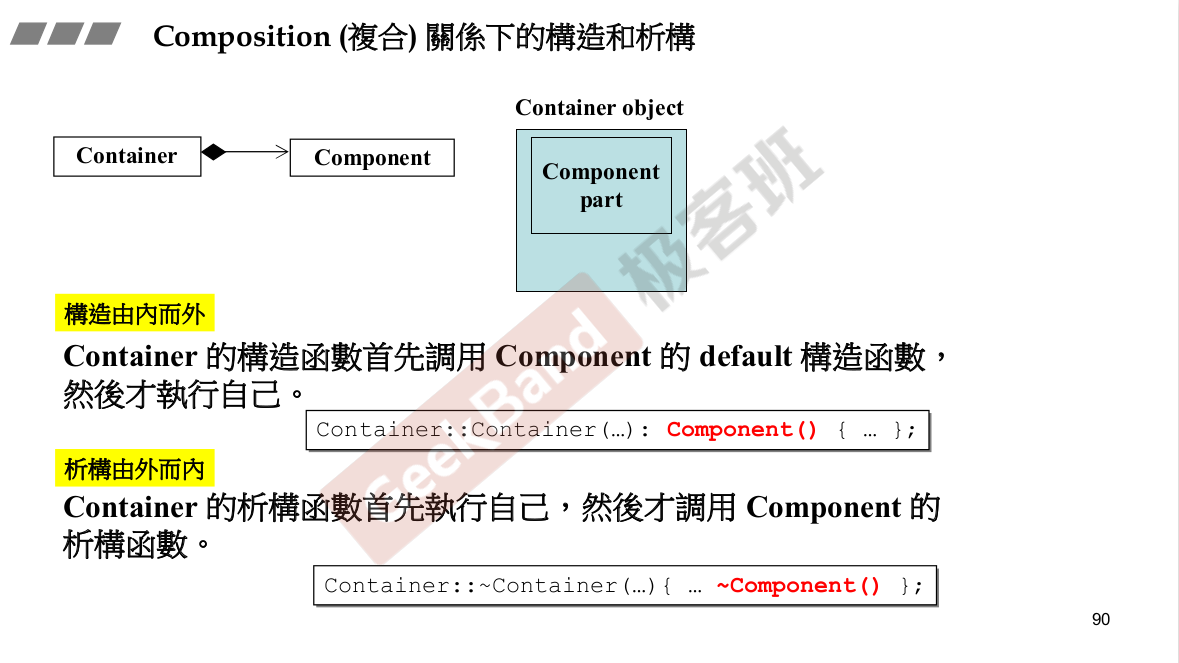
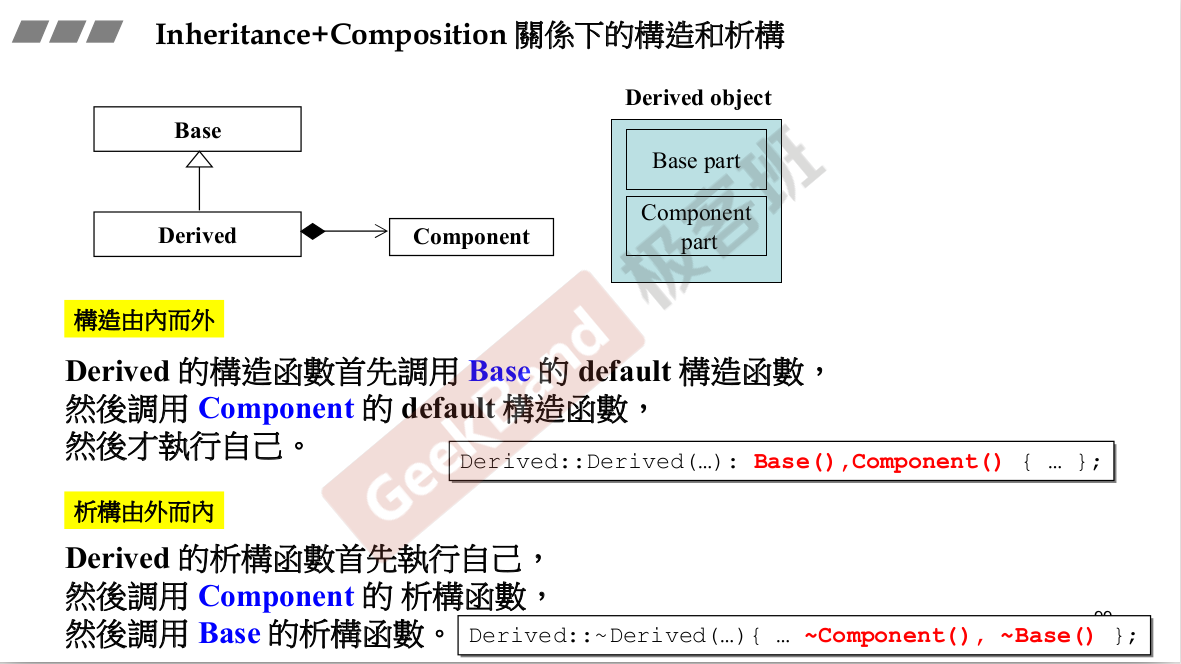
构造由内而外,析构由外而内。
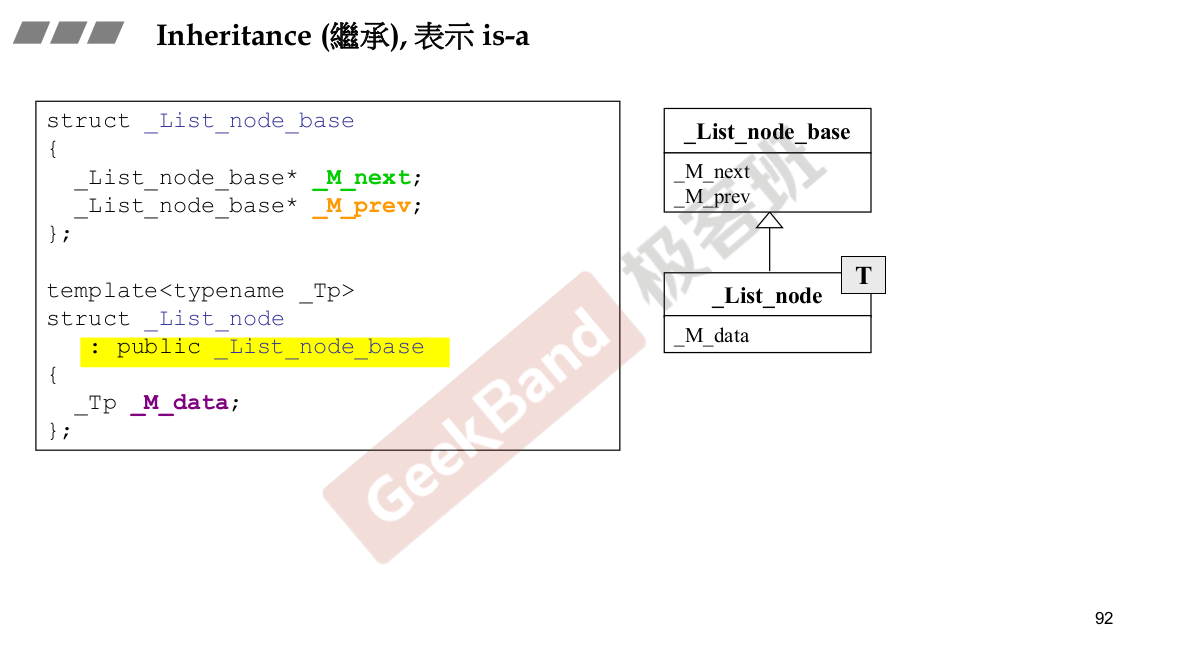
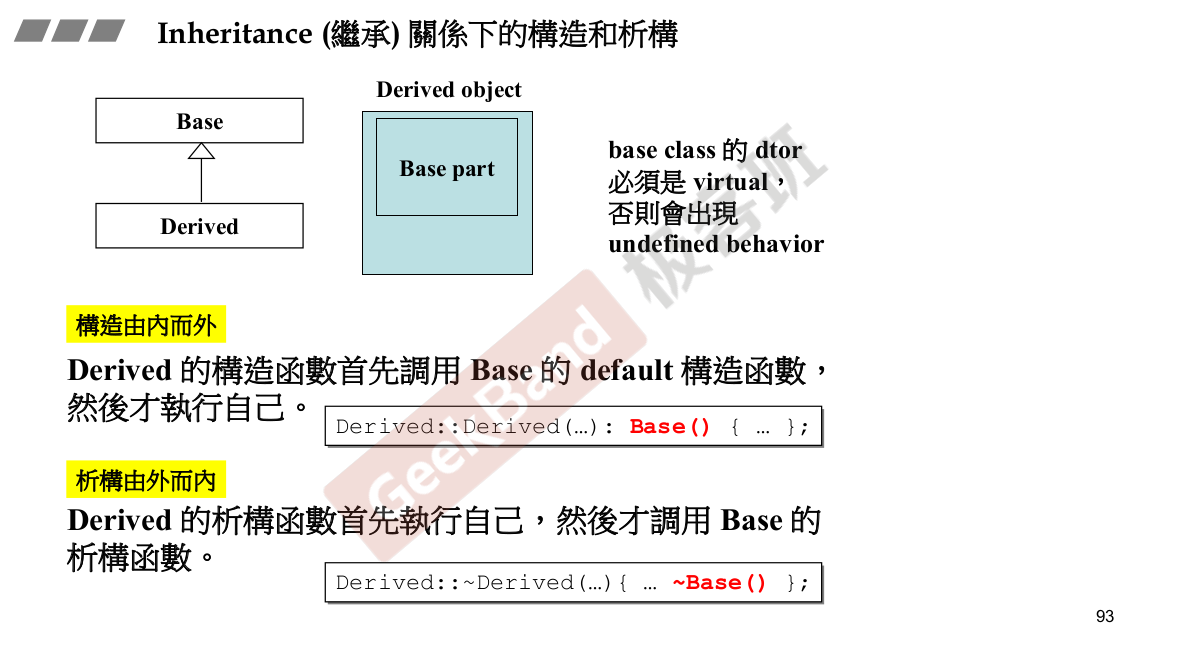
父类的析构函数必须是virtual.

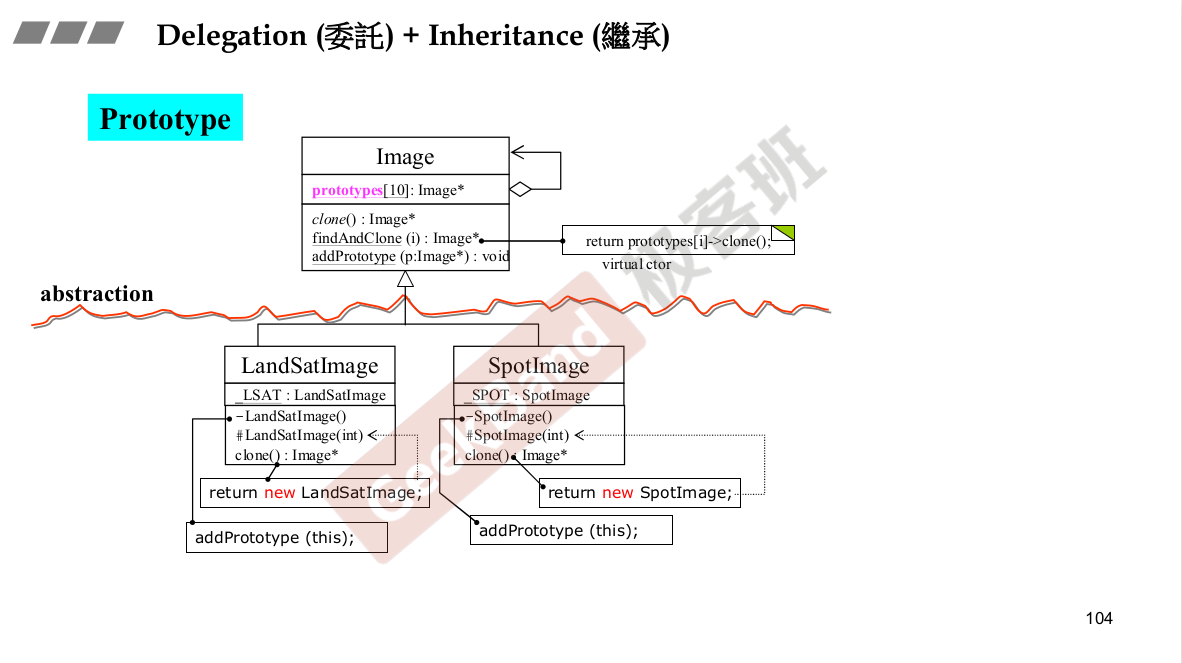
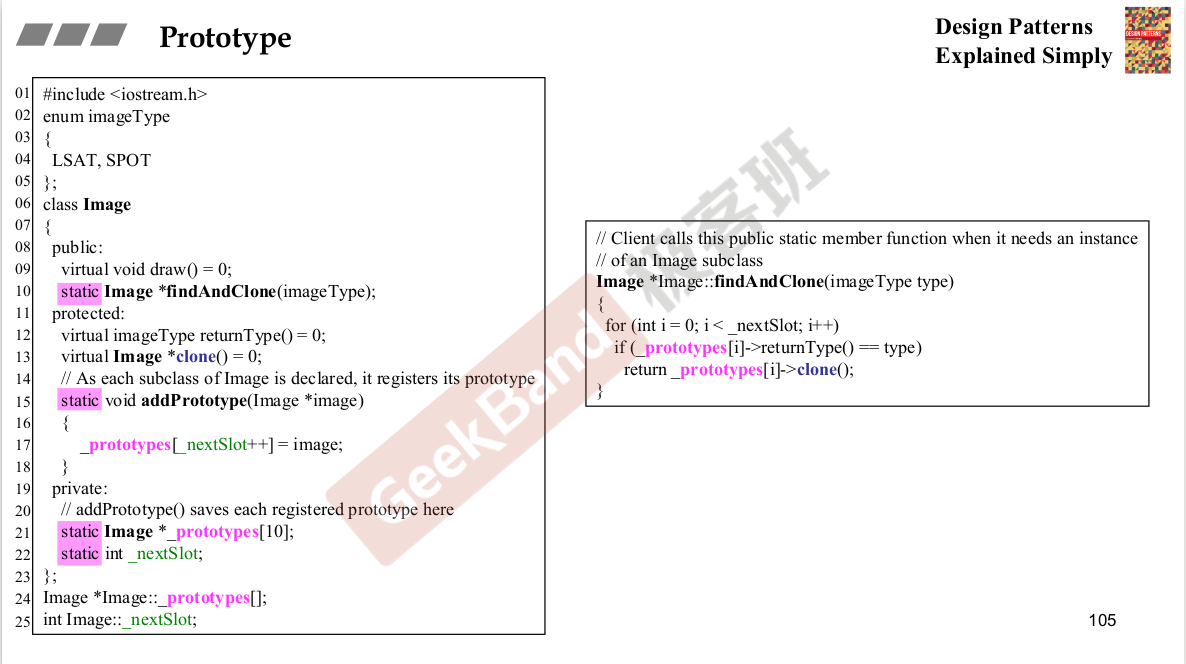
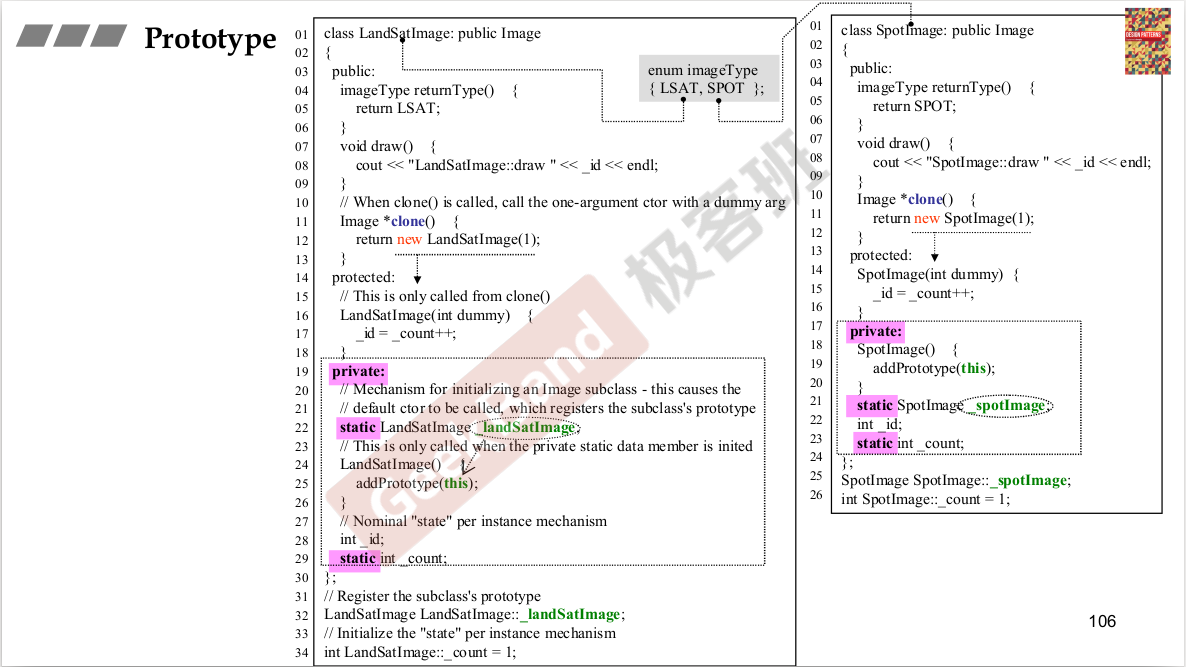
纯虚函数:子类一定要去重新定义他,父类并没有去定义。这也是一种设计模式。
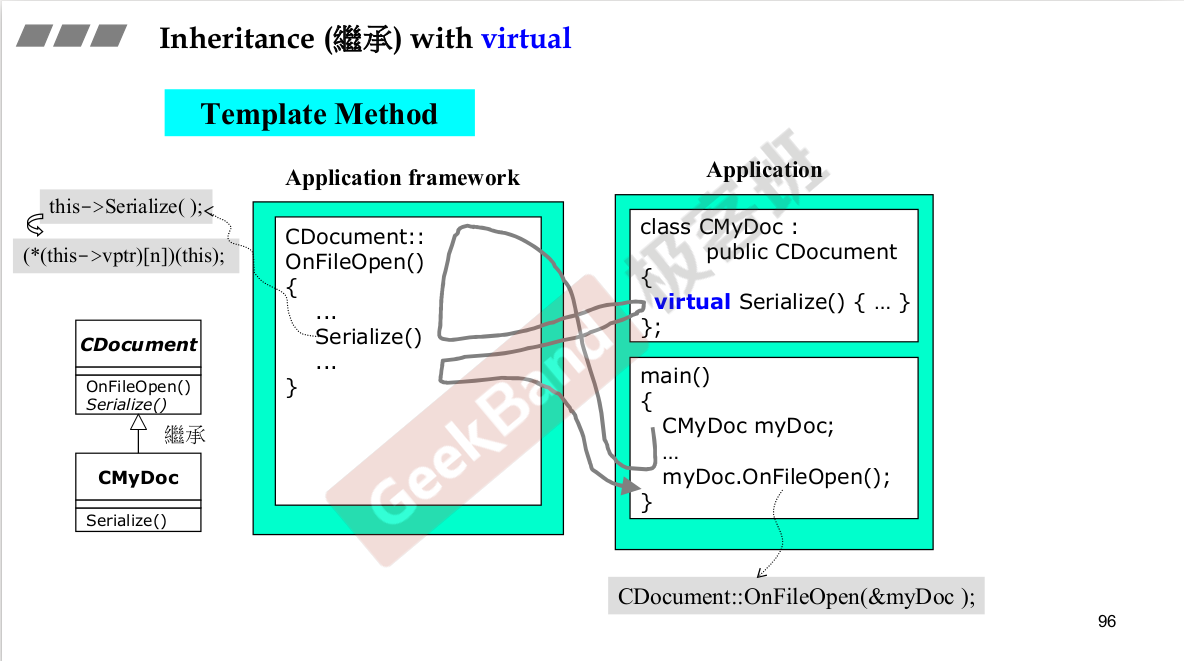

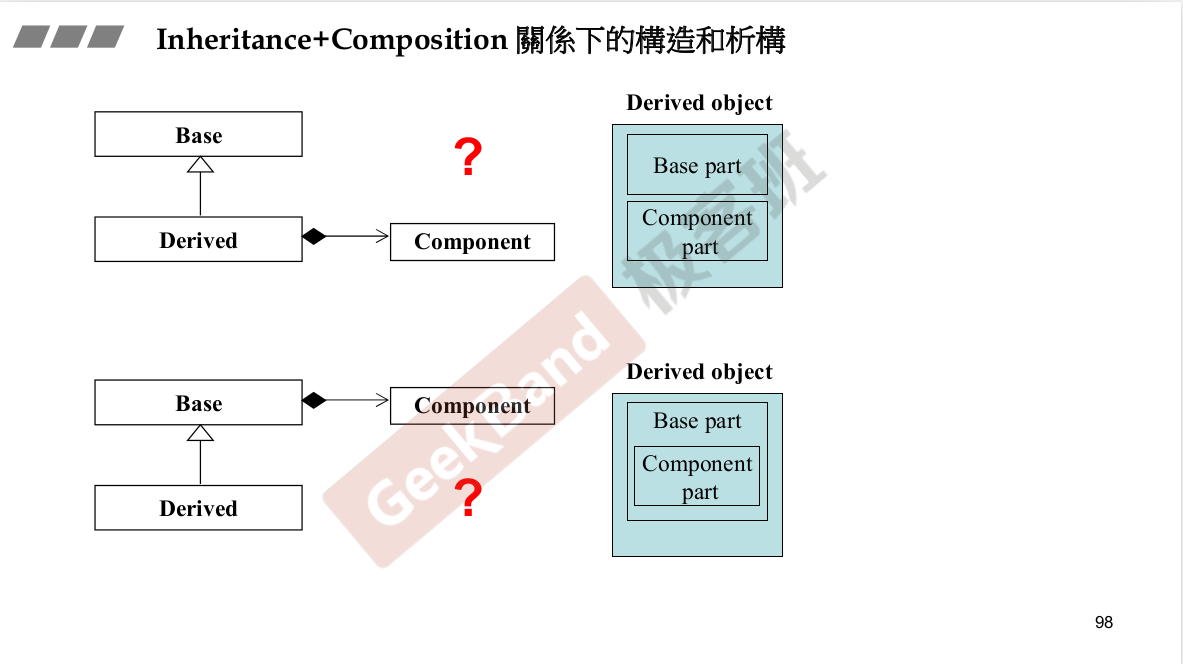
既有继承,又有复合,构造时候谁先?